Addtime: 2020-07-16 Browse times: 3899
"Vacuum" literally means empty. However, in physics, this seemingly empty concept has extremely rich and fascinating content.
In the 19th century, the popular view of physicists was that "the vacuum is filled with ether". Intuitively, volatility needs some kind of medium. Since electromagnetic waves can travel throughout space, a special medium, namely ether, should be permeated in the universe.
Aristotle believed that all things in the world are made up of fire, water, earth and air, and the fifth element, ether, is full of the universe.

However, the famous Michelson Morey experiment denied the existence of this ether. In 1905, Einstein put forward the special theory of relativity, abandoning the concept of ether: electromagnetic field itself is a kind of matter, electromagnetic wave is its form of motion, without relying on the medium of ether, it can spread in space.
The first quantum revolution gave birth to quantum mechanics, which opened the door to the micro world and endowed vacuum with more abundant physical contents.
In 1920s, Dirac proposed that "vacuum is an electronic sea". He believes that a vacuum can be seen as a sea filled with electrons of all negative energy states, and electrons with positive energy that we usually see move on the sea surface.
In 1950s, Feynman and others put forward the concept of "vacuum fluctuation". They believe that there are a large number of virtual photons and electron positron pairs in the vacuum. Electrons move in such a vacuum background, as if wrapped in a garment formed by various vacuum fluctuations.
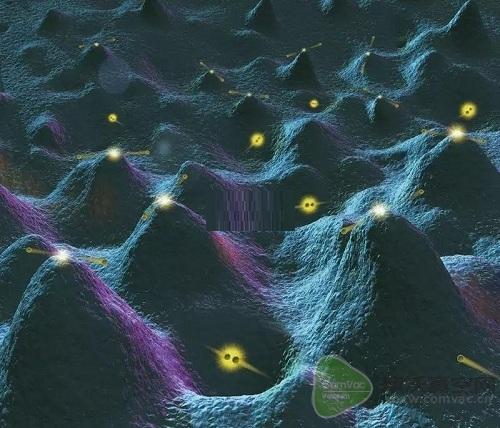
The image is the schematic diagram of particles and anti particles constantly produced and disappeared due to "fluctuation". Peaks represent high-energy States, forming particles and antiparticles in pairs. The newly generated particle disappears instantly after colliding with the antiparticle. At the micro scale, a vacuum without any substance is also a boiling world.
In the 1960s, many Nobel laureates including Weinberg put forward the concept of "vacuum spontaneous symmetry breaking". They believe that the motion of the system has some symmetry, but the ground state or vacuum state of the system does not. The universe is full of Higgs field, and its spontaneous symmetry breaking gives the mass of everything. The origin of mass is one of the most fundamental problems in physics, and vacuum plays a central role here.
In the 1970s, several famous physicists proposed the concept of "vacuum condensation and vacuum phase transition". Just as water has several phases, such as solid, liquid and gas, phase transition can occur through temperature change. They believe that at lower energy, vacuum is in condensed phase, while at very high energy, vacuum can change phase and produce a new state of matter.
Since the 1990s, the research of quantum information has set off the second quantum revolution. The basic unit of quantum information is qubit, which can be in any superposition state of two basic states. Multiple qubits can form what Einstein called "ghost like telepathy". Even if the entangled particles are far apart in space, they have quantum correlation, which is called quantum nonlocality. The study of the concept of vacuum from the perspective of quantum information provides a new opportunity to answer the basic physical problems.
Wheeler once put forward a thought-provoking conclusion: "everything comes from bit". This view holds that information is very basic. Everything in the universe (including any particles and fields, even space-time) originates from the basic unit of information - bit. After the rise of the research on quantum information, this argument has been upgraded to "it from qubit". This is a new form of ether theory - quantum ether. Many scholars have studied this interesting and very important concept.
Some scholars, including the author, put forward that "it is not enough to construct the theory of everything only by considering quantum bits (i.e. binary theory)" From the experiment, we find that there is stronger than the existence of binary correlation in quantum mechanics, or the multi value problem can not be realized by decomposing into binary. This touches on a crucial issue - the theory of everything must be built on the basis of quantum entanglement of multi valued correlations.
Some scholars have proposed that "the structure of space-time originates from quantum entanglement". On the one hand, physicists use the entanglement entropy to express the quantum entanglement. The entanglement entropy of many quantum systems is proportional to the size of its boundary. On the other hand, gravity has similar properties. For example, the entropy of a black hole is proportional to the surface area surrounding the region. Interestingly, the area law of entanglement entropy is closely related to the entropy of black holes. This inspires people to place the hope of understanding the essence of space-time on its connection with quantum information.
These scholars further speculate that there is a passage connecting two different spatiotemporal regions, namely wormholes. Quantum entanglement creates wormholes, which connect two entangled particles far away. Therefore, the structure of space-time originates from quantum entanglement, and the change of quantum entanglement changes the structure of space-time and produces gravitation. From the perspective of quantum information, it is possible to deepen the understanding of space-time and the origin of the universe.
Some physicists, including Wen Xiaogang, have proposed that "vacuum is a sea of quantum bits". If we compare these qubits to water molecules, the long-range entanglement of qubits is like water molecules forming a string. These strings are filled in the whole space

Scan QR code and add wechat